Exporting Quix data to Jupyter Notebook
In this documentation, you learn how to use Jupyter Notebook to analyze data persisted in Quix.
Legacy features
Some of the features on this page are not available to new users, including those related to the Quix Data Explorer and the topic Persistence feature. However, legacy users may still have access to these facilities.
Why this is important
Although Quix is a real-time platform, to build real-time in-memory models and data processing pipelines, you need to understand data first. To help with that, Quix offers the option to persist data in topics. This data can be accessed using the Query API. This helps make data discovery and analysis easier.
Prerequisites
You'll need some data stored in Quix. You can use any of the Quix data sources available in the Quix Code Samples.
You can also follow the onboarding process after you login for the first time. The onboarding process helps you create your first source.
Start for free
Book a session with us to start for free.
We will create a time-limited free account for you, and our experts will help you get started with your specific use case.
You also need Python 3 environment set up in your local environment.
Install Jupyter Notebook as directed here.
Create a new notebook file
You can now run Jupyter from the Windows start menu, or with the following command in an Anaconda Powershell Prompt, or the equivalent for your operating system:
Then create a new Python 3 notebook:
Connecting Jupyter Notebook to persisted data
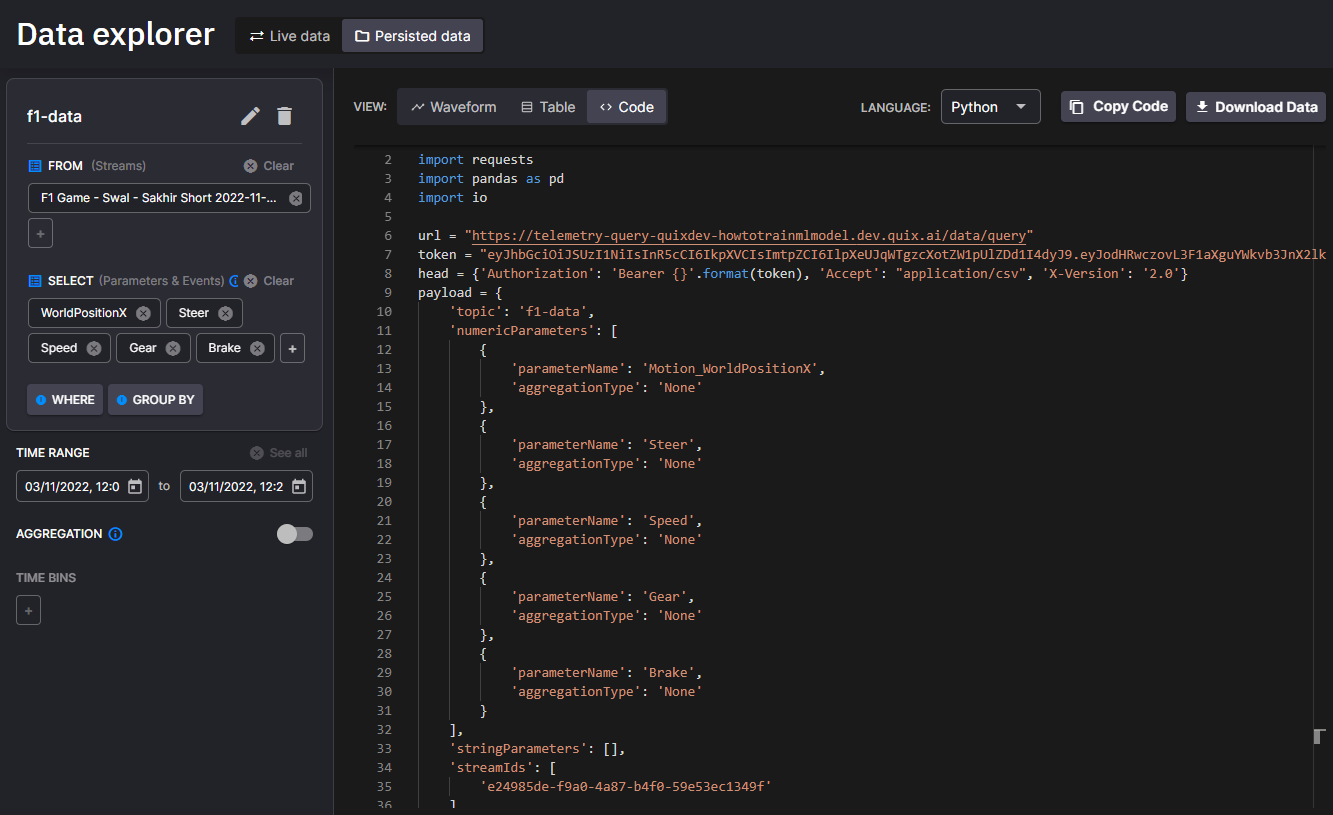
The Quix web application has a Python code generator to help you connect your Jupyter notebook with Quix.
You need to be logged into Quix for this. To import persisted data:
-
Select an environment.
-
In the main left-hand navigation, click
Data explorer. -
Add a query to visualize some data. Select parameters, events, aggregation and time range.
-
Select the Code tab.
-
Ensure Python is the selected language:
-
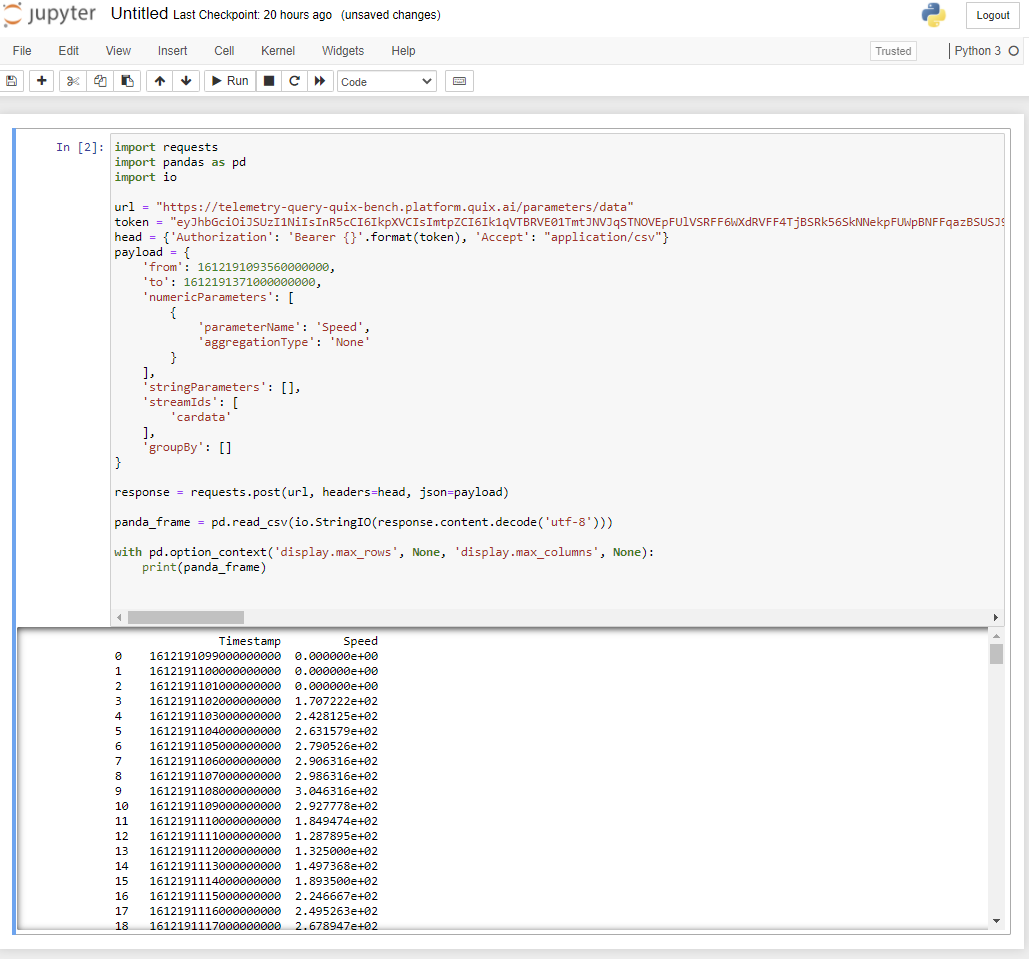
Copy the Python code to your Jupyter notebook and click
Run:
Tip
If you want to use this generated code for a long time, replace the temporary token with a Personal Access Token.
Too much data
If you find that the query results in more data than can be handled by Jupyter Notebook, then try using the aggregation feature to reduce the amount of data returned.
For more info on aggregation you can watch this short video.